Palo Alto HA Overview
Ahmet Numan Aytemiz , 10.03.2021
- High Availability Provides
- Redundancy
- Business Continuity
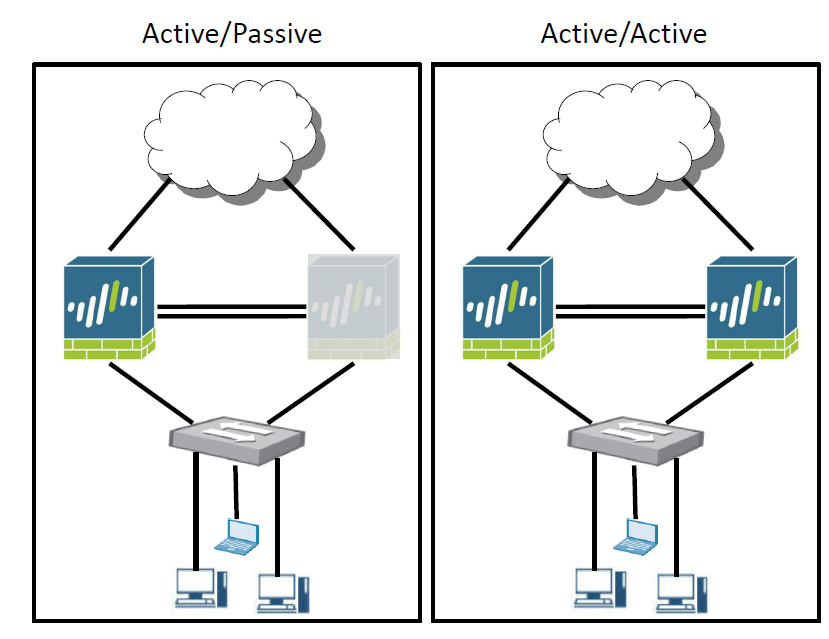
- HA has two deployment modes:
- Acitve / Passive
- Active / Active
- Firewalls synchronize their configuration
- Networks, objects, polices, certficates, session table
- Firewalls not syncronized:
- Management interface configuration, HA settings, logs and ACC information
Active / Passive High Availability
- One firewall actively manages traffic while the other is syncronized and ready to transition to the Active state should failover
- In this mode , both firewalls share the same configuration settings, and one actively manages traffic until a failure occur
- Active/Passive HA does not increase the session capacity or increase network throughput.
- Active/Passive HA is supported in Virtual Wire, Layer 2 and Layer 3 deployments
Active / Active High Availability
- Both firewalls in the pair are active and processing traffic
- Both firewalls individually maintain session tables and routing tables and syncronize to each other
- The active/active configuration primarily designed to support environments that require asymmetric routing
- Active/active HA is supported in Virtual Wire and Layer 3 deplyments
HA Prerequisites
- Before HA can be enabled, both firewalls must have the same ;
- Model
- PAN-OS version
- Up-to-date application, URL and threat databases
- HA interface type
- Licences
- Matching slot configuration (multi-slot firewall models)
- For VM Series firewalls, both firewall must have the same;
- Hypervisor
- Number of CPU cores
HA Components and Operation
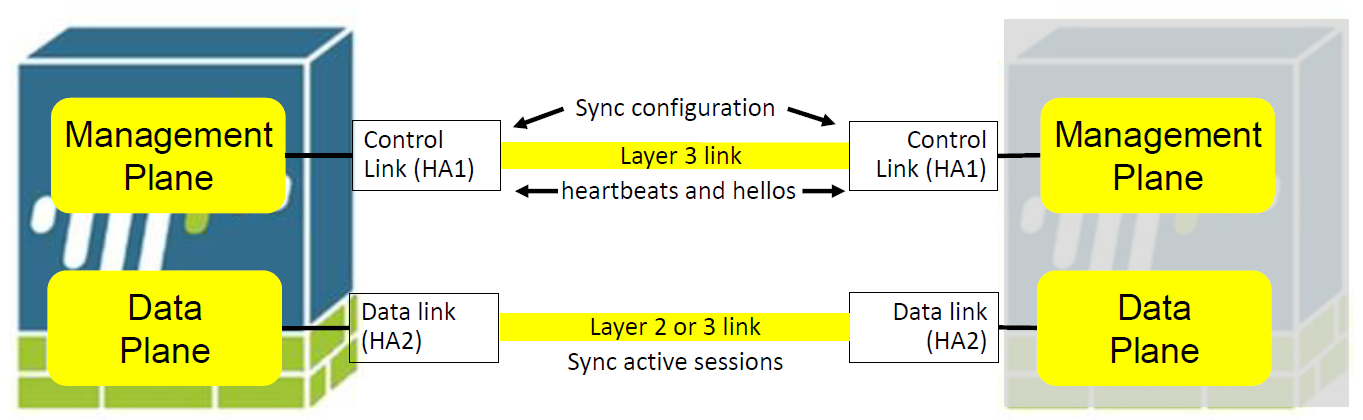
Active/Passive HA Links
- The Control link is a layer 3 link and requires an IP address
- Used to synronize routing and user-id information between management planes
- The active firewall also uses this link to syncronize configuration changes with its peer firewall
- If you will use mgmt interface as a control link, allow icmp packets on the managements interface
- The Data link is used to syncronize sessions, forwarding tables, IPSEC security associations, and ARP tables between firewall in an HA pair.
- Unidirectional flow from active to passive firewall
Dedicated and Non Dedicated HA Ports
- Dedicated HA Ports:
- PA-800, PA-3000, PA-3200, PA-5000 and PA-7000 Series
- Non Dedicated HA ports:
- PA-200 and PA-500 series
- VM series
- For Control Link Uses mgmt or eth n/n, for Data Link (eth n/n)
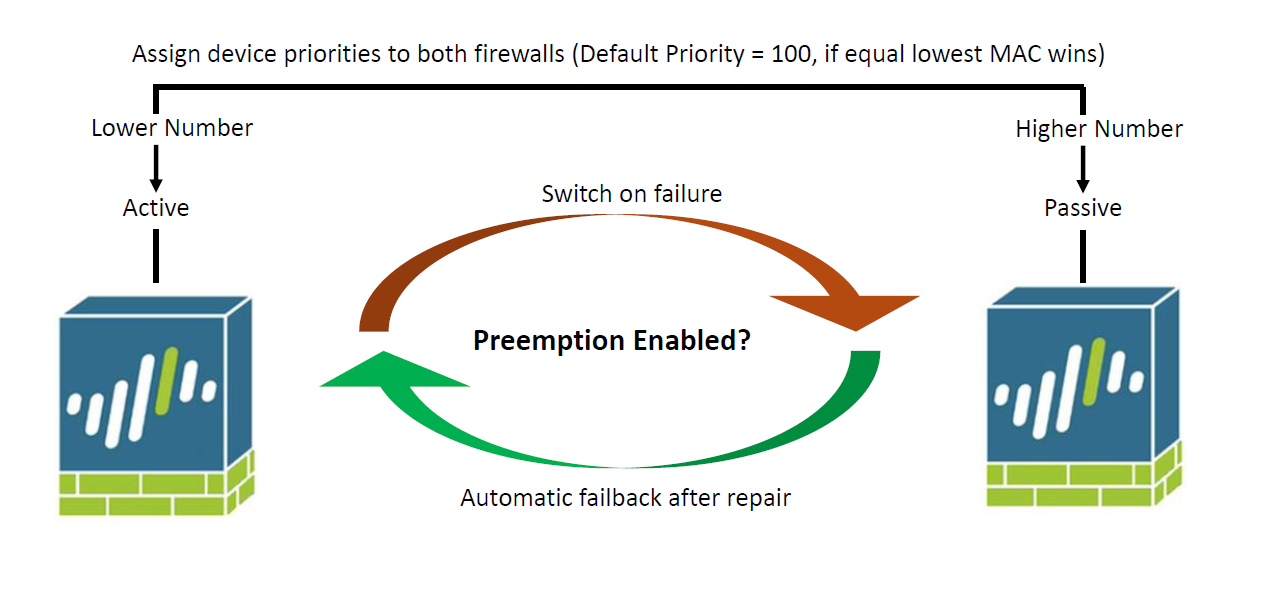
Designating an Active Firewall
- Lower priority number win
- If priorities are equal , lowest MAC wins
- default priority = 100
Failure Detection
A firewall uses several monitored metrics to detect failure :
- Hello messages and heartbeats to verify that the peer firewall is responsive and operational
- Monitor the link states of its phsical interface
- monitor to paths to mission-critical IP address using ICMP pings to test reachability
- failover can occur when an internal health check fails
Active / Passive Firewall States
- Initial : HA Neogitiations begin
- Active : Normal traffic-handling state
- Passive : Normal traffic is discarded; might process LLDP and LACP traffic
- Suspended : Administratively disabled
- Non-functional : Error state
Monitor Firewall States
The state of the individual firewalls in an HA pair can be monitored from the Dashboard tab of the web interface
- Green –> good
- Yellow —> passive
- Red —> critical
System Log
- Use the system log entries to troubleshoot HA configuration
(subtype eq ha)